Table of contents
According to the report, published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly half of Americans (47.2%) of adults aged 30 years and older suffer from some form of periodontal disease — commonly known as gum disease. When caught early, gum treatment is relatively easy. The chances of getting exposed to periodontal disease increase with age. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention claim that 70.1% of adults aged 65 and older have periodontal disease.
Your family dentist can reverse the sometimes-devastating consequences of gum disease when it’s caught early enough. More severe periodontal disease may require more involved procedures, such as:
Gum treatment is necessary to fight periodontal disease. Gum disease is an infection caused by the growth of harmful bacteria in your mouth. It’s usually the result of insufficient brushing or flossing, which allows plaque and tartar to build up along the gum line. Your family dentist may notice early signs of periodontal disease, including bleeding or sore gums, at a routine dental visit.
Signs of a more advancing disease that require gum treatment include:
Left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss. If the infection becomes abscessed, it can cause intense pain. It’s important to see your dentist right away for gum infection treatment if you experience any of the above symptoms.
If you notice that your gums are looking redder than the healthy pink they should be, see your general dentist. If your gums are bleeding a bit when you brush your teeth, chances are you have gingivitis, an early form of periodontal disease.
Gum infection treatment for gingivitis starts with a thorough cleaning at your family dentist’s office. This cleaning may be mildly uncomfortable, but the pain is rare. The leading dentist takes care to remove stubborn tartar as gently and painlessly as possible.
Following the professional cleaning, treatment for gingivitis continues at home. Brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day. Consider using an angled toothbrush and floss picks with long handles so you can reach the teeth in the back of your mouth. An updated dental hygiene routine can reverse the effects of gingivitis and keep it from coming back.
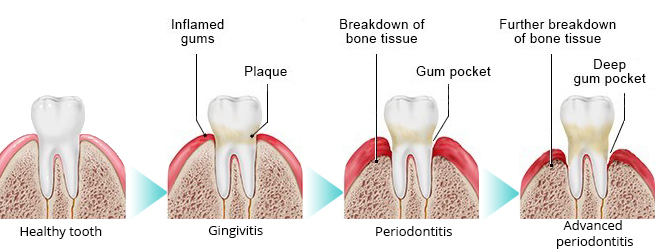
Left unchecked, gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, a more serious infection of the gums. Periodontitis can lead to pockets of infection under the gum line or painful abscesses. Periodontitis can affect the ligaments and bones that support your teeth, eventually causing your teeth to become loose and fall out. Gum abscess treatment usually begins with a course of oral antibiotics.
Once the acute gum infection has been treated, the next steps can take place:
The side effects of dental cleanings and scaling and root planing are few. You may feel mild discomfort during or after the procedure. Your dentist may recommend over-the-counter pain relief. You can usually resume eating as usual within a few hours following the procedure.
As with any surgery, no matter how minor, pocket reduction and grafts carry some risks, including:
Once the treatment is complete, your dentist may see you for more frequent visits to ensure the disease doesn’t return. Pay attention to his recommendations and develop smart dental health habits.
The most common gum disease signs and symptoms are swollen, red, and bleeding gums. Gum bleeding normally occurs during teeth cleaning. But your gums may bleed for no apparent reason too. In general, gingivitis does not cause any symptoms or pain. Hence, it may remain undetected for some time.
Periodontitis does not cause any symptoms until it becomes advanced. Along with bleeding and red gums, you might also experience sensitive teeth, receding and sore gums, and bad breath. In case your gums become inflamed, they may start pulling away from the neck of the tooth. This will lead to the formation of the gaps between the gums and the teeth, known as gum pockets.
The only reliable way of detecting gum disease is by visiting a dentist on a regular basis. During a dental check-up, your dentist will also perform a gum disease evaluation. Your mouth will be inspected for possible gum pockets using special equipment called a periodontal probe. In case a dental specialist detects signs that you have gum disease, a more thorough examination will be needed. X-rays will help find out if any bone tissue has been broken down.
Even though plaque develops very quickly, it can be easily removed by cleaning your teeth thoroughly and regularly. Dental floss and interdental brush can help you clean your teeth properly. If you don’t practice proper dental hygiene, plaque can harden and develop into tartar. It can only be removed by your dentist during a dental check-up. Insurance carriers do not cover plaque and tartar removal. Hence, you will have to pay for these services yourself.
Do you have any questions about the gum disease treatment? For more information or to schedule an appointment with the best cosmetic dentist Khabensky DDS of Family Cosmetic & Implants Dentistry of Brooklyn please contact our dental clinic.